
8 minút
KYRGYZ LOCAL ELECTIONS IN SOCIAL MEDIA
A popular singer dominated on Instagram, while on Facebook it was the former mayor of Bishkek.
Local elections were seen as a rehearsal for the parliamentary elections after the constitutional reform
[photo credit - eurasianet.org]
Between 12 March 2021 and 9 April 2021, Media Development Center, a Kyrgyz media organization, and MEMO 98, a Slovak non-profit specialist media-monitoring organization, monitored social media in the run-up to the 11 April local elections.
The main purpose of this monitoring was to determine the impact of social media on electoral integrity and the extent to which social media provide important information that voters need in their decision-making. Television is the primary source of information about politics, but the growing relevance of social media has to be acknowledged, and so we continued with the monitoring of Facebook and Instagram. We were interested in determining to what extent are social media used in Kyrgyzstan during elections. MEMO 98 and Media Development Center (MDC) monitored social media prior to the 4 October parliamentary elections as well as the 10 January 2021 early presidential election.
There are an estimated 2.5 million social media users in Kyrgyzstan which is approximately 40 percent of the population (comparing to 22 percent of social media users in the Central Asia region), with a 2.1 million Instagram audience and 610,000 Facebook audience (people that can be reached by either Facebook or Instagram ads on the respective platforms).
The monitoring included Facebook and Instagram accounts of actors within four categories (politicians, political parties, authorities, and media). Out of the initial list of 25 political parties that were contesting local elections in the capital Bishkek, leaders of these parties and president Japarov; 3 officials, local election-related, authorities, the monitoring eventually included those actors who had public pages or accounts on Facebook and Instagram at the time of the monitoring. Such accounts were found for 8 politicians, 21 political parties, and 3 official institutions on Facebook, and 22 politicians, 20 political parties, and 2 official bodies on Instagram.
Politicians, parties, official authorities produced a total of 2,519 posts on Facebook and 2,153 on Instagram. These posts generated as many 286,407 interactions on Facebook and 1,816,570 on Instagram.
#Findings
The monitoring was conducted from 12 March until 9 April 2021. It focused on 32 public accounts of political subjects (politicians, political parties, official institutions) across Facebook and 44 such accounts on Instagram.
Monitored Facebook accounts of political actors produced a total of 2,519 posts, with as many as 1,819 posts produced by political parties, 212 posts by politicians, and 488 posts by authorities. All these Facebook posts of political actors generated as many as 286,407 interactions.
Instagram accounts of monitored political actors produced a total of 2,153 posts - so even with the higher number of accounts on Instagram, the number of posts was smaller than on Facebook. This number included 1,631 posts by political parties, 361 by politicians, and 161 by authorities. All Instagram posts together generated as many as 1,816,570 interactions. The interaction rate on Instagram is generally higher than on Facebook (this was noted also in previous elections); Instagram posts saw about 6 times as many interactions as Facebook’s posts.
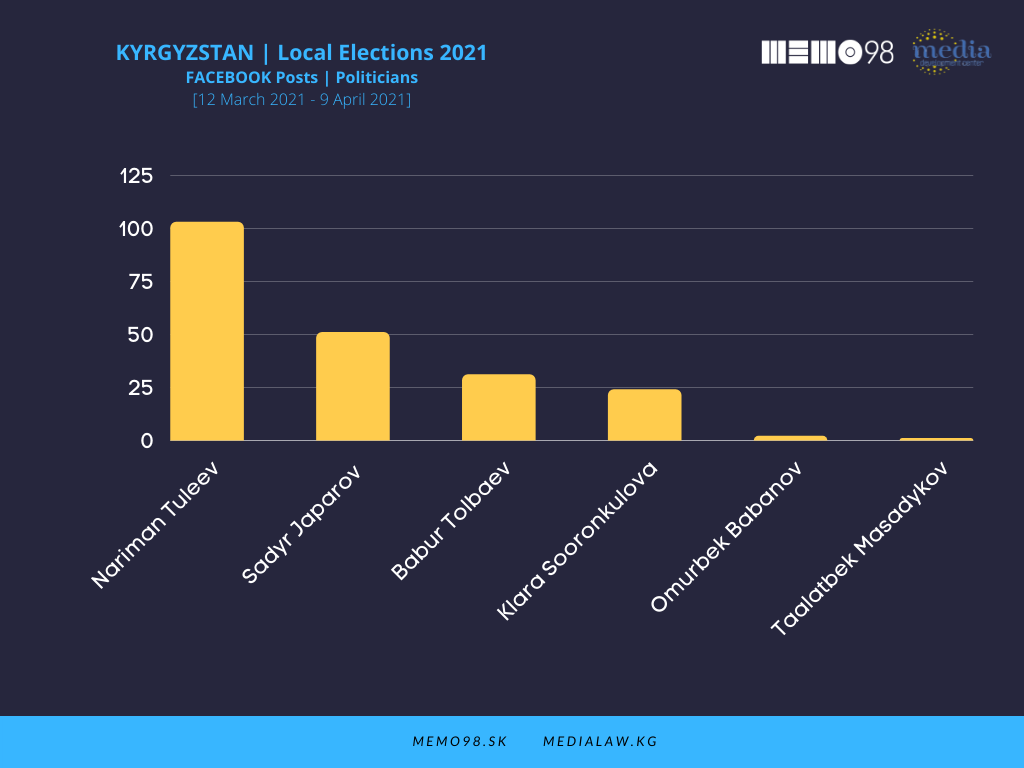
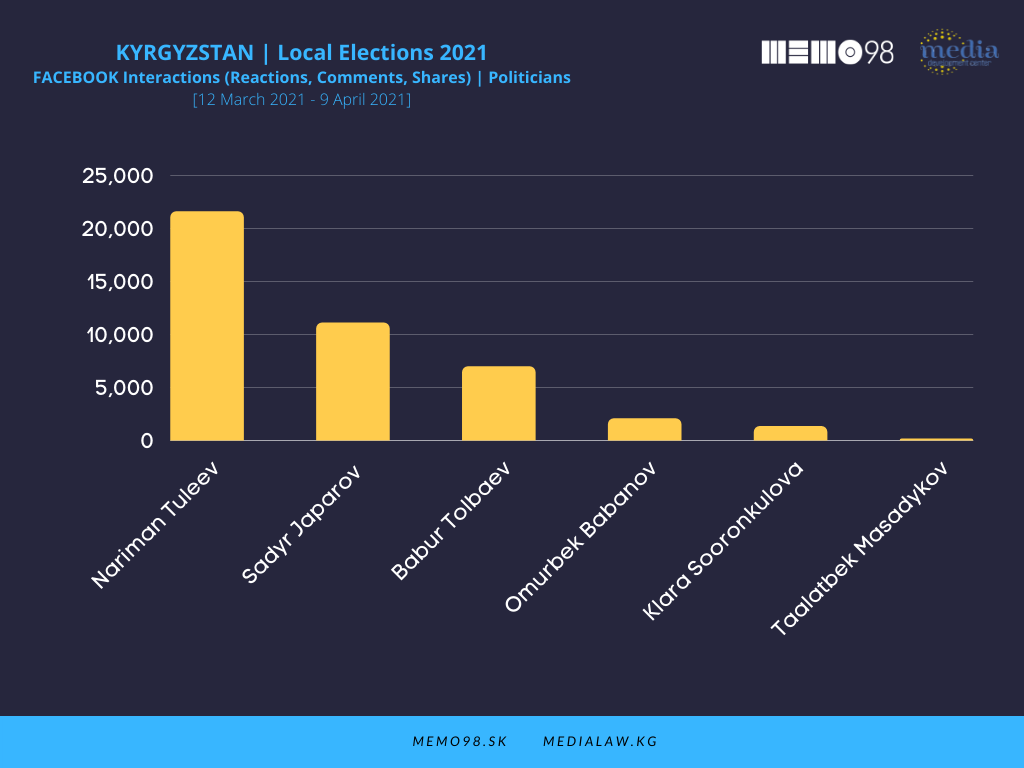
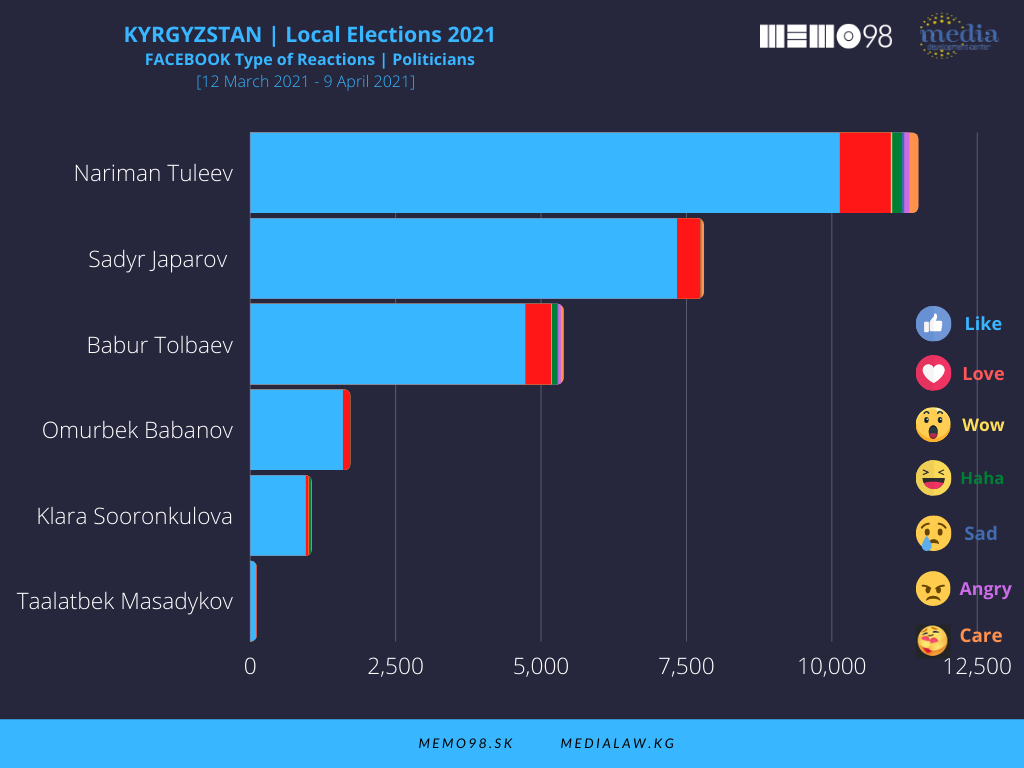
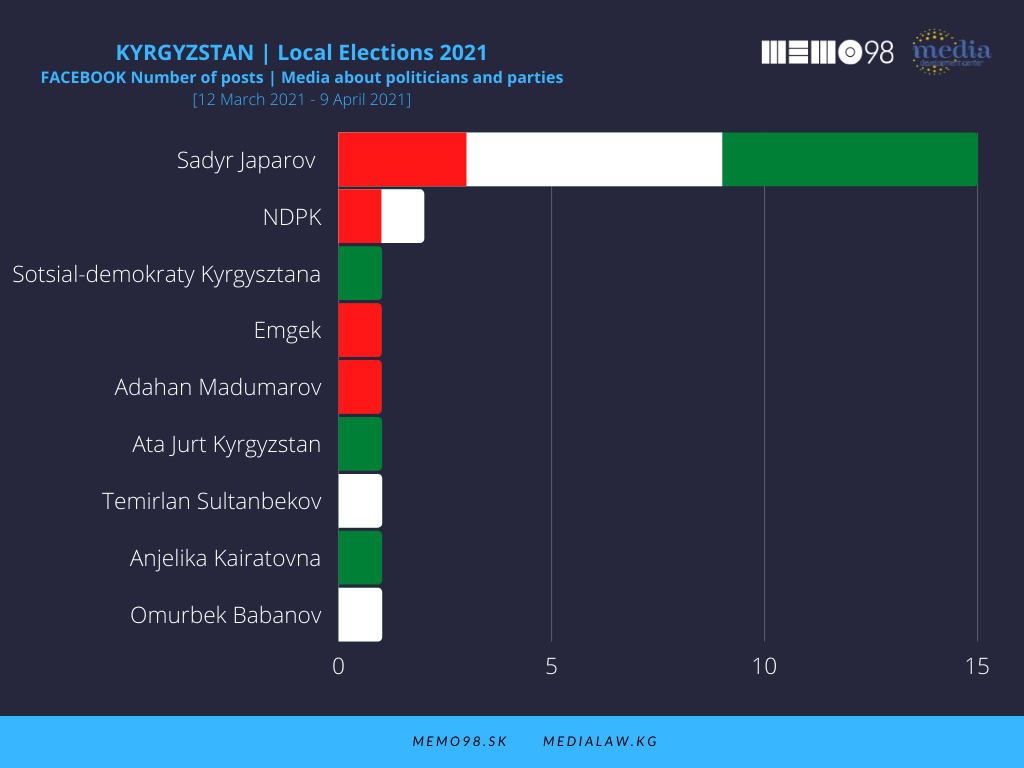
On Facebook, among the key politicians (out of 8 profiles monitored), the most active one was N. Tuleev (103 posts) followed by President S. Japarov (51 posts) and B. Tolbaev (31 posts). These politicians dominated also in terms of interactions, with the following figures: Tuleev (21,578), S. Japarov (11,090), and B. Tolbaev (6,957), followed by O. Babanov (2051) and K. Soorunkulova (1,324).
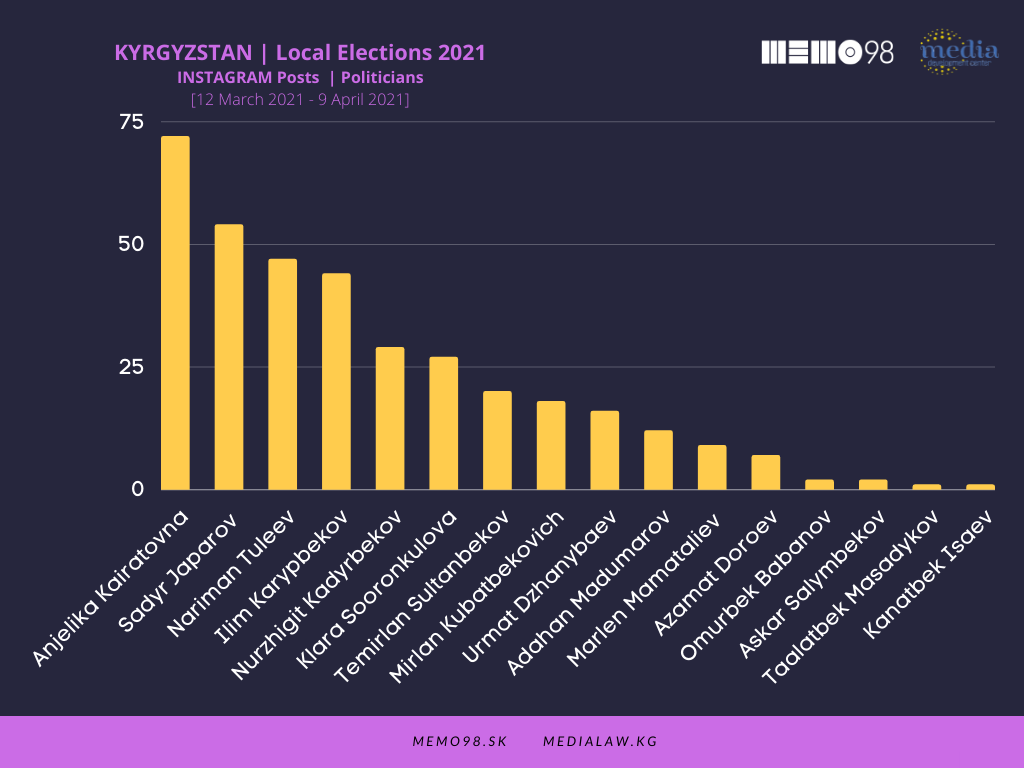
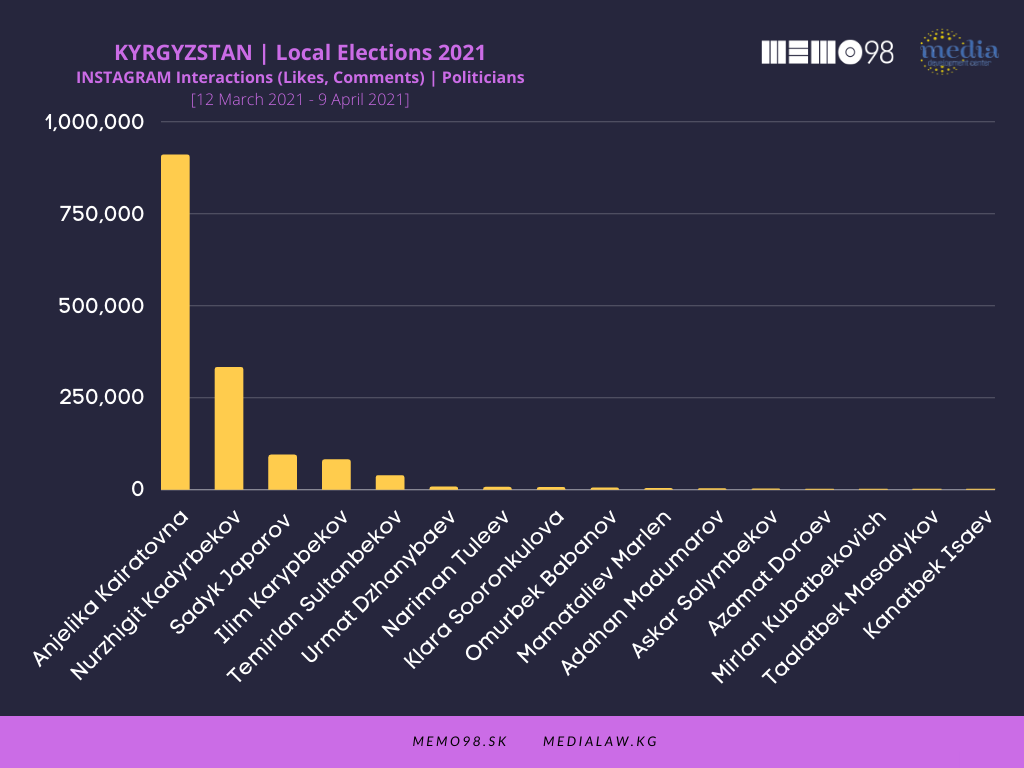
Same politicians were also very active on Instagram, with the most active one being Anjelika Kairatovna (72 posts), followed by president Japarov (54 posts), N. Tuleev (48 posts), and I. Karypbekov (44 posts). In terms of interactions, A. Kairatovna dominated with more than 910,000 followed by N. Kadyrbekov (332,000) and S Japarov (less than 94,000). In the run-up to the 10 January 2021 presidential election, Anjelika Kairatovna produced the most popular Instagram posts (at that time as a social media influencer).
Of 21 accounts of political parties followed on Facebook, 8 produced more than 100 posts. The most active party was Ak Bata (209 posts) followed by Emgek (200 posts) and Respublika (183 posts). In terms of interactions, Tynchtyk was the most effective, as its 116 posts received 37,000 interactions. Respublika followed with 33,000 interactions and Yntymak was third with 29,000 interactions.
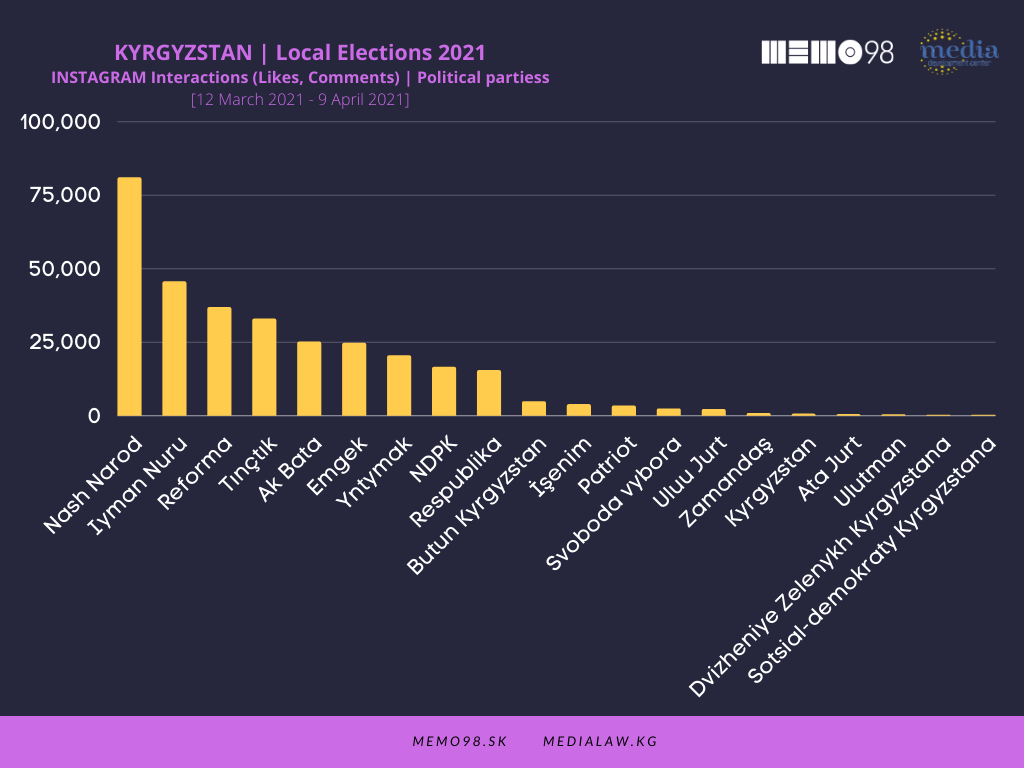
On Instagram, parties generated a smaller number of posts compared to Facebook (1,631 vs 1,819, respectively). Iyman Nuru was the most active with almost 200 posts produced, followed by Reforma (175) and Respublika (156). In terms of interactions, Nash Narod clearly dominated with 80,000 interactions (only with 70 posts), followed by Iyman Nuru 45,000), Reforma (36,000), and Tynchtyk (33,000).
The Bishkek City Hall was by far the most active among the three authorities monitored, on both platforms. On Facebook, it produced over 376 posts and 124 on Instagram.
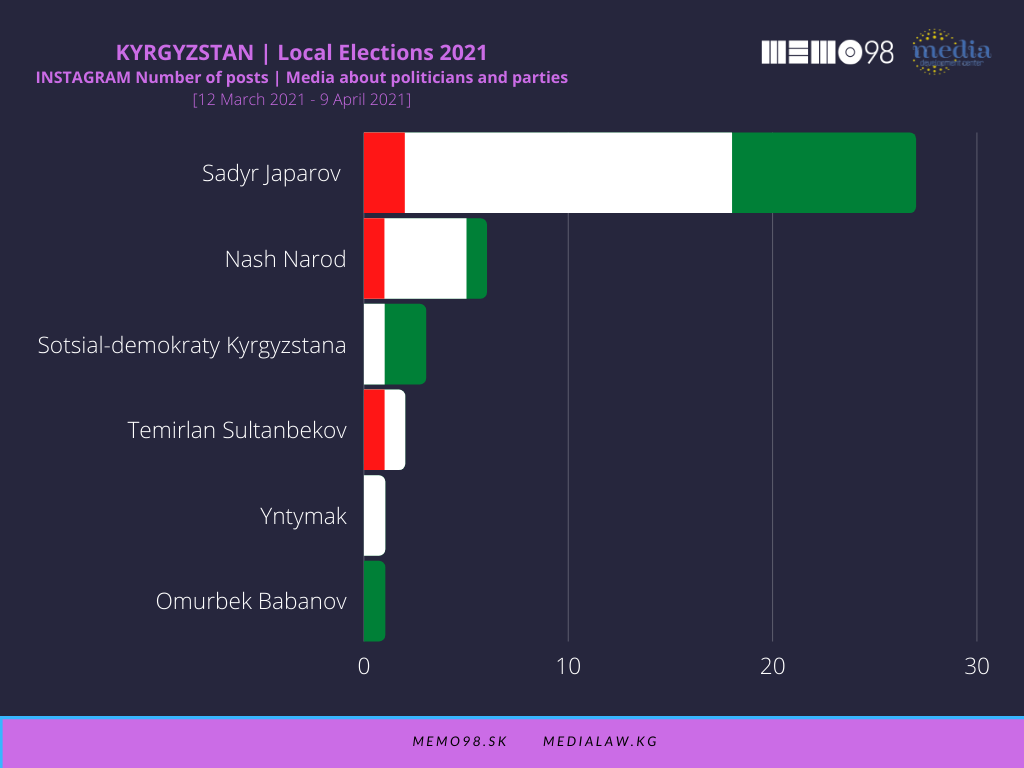
For the monitored media, of some 200 posts with the highest interaction rate on each of the two platforms, only a relatively small number of posts dealt with political issues. In Facebook and Instagram, there were only 24 and 40 such posts respectively. The incumbent president Japarov was clearly in the center of the monitored media focus, as roughly two-thirds of political posts were dedicated to him. More specifically, he was the subject of 16 Facebook and 27 Instagram posts and was portrayed mainly in a neutral way.
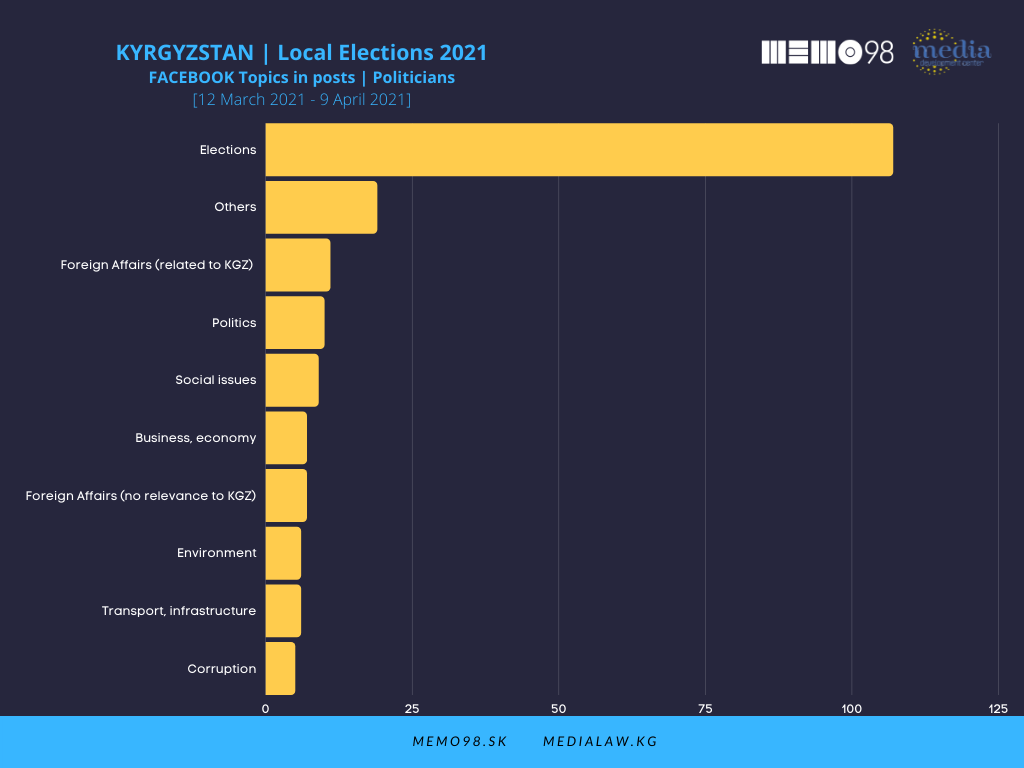
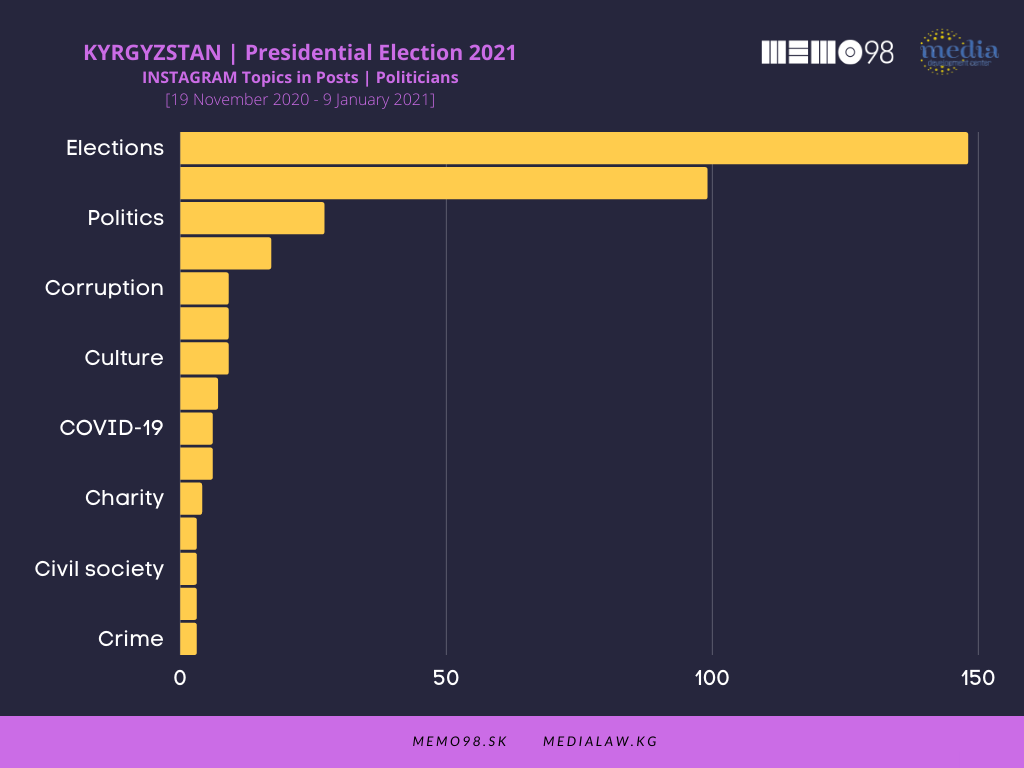
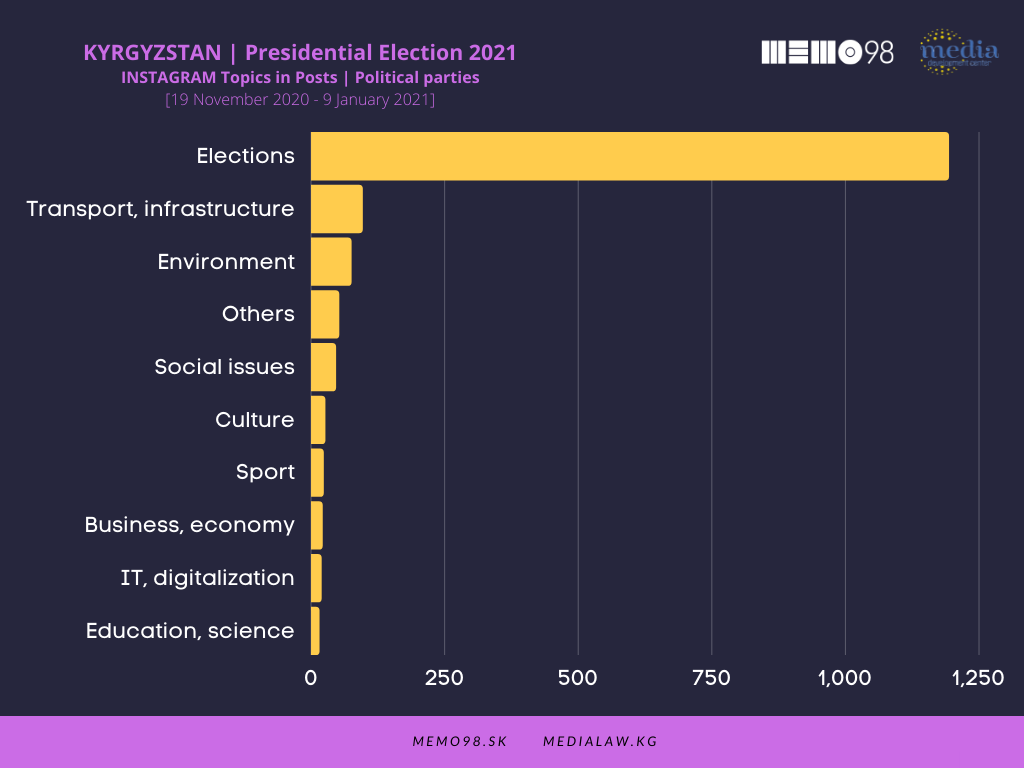
Elections as the main topic overwhelmingly dominated in posts by politicians and political parties, both on Facebook and Instagram. The Bishkek and Osh City Halls focused on issues related to transport and infrastructure. In the media’s posts with the highest interaction rate, topics related to elections and politics were not at the center of the media attention. The issues dominating the media posts on both platforms were Foreign affairs, COVID-19, and Social issues.
Political actors used advertising on the Facebook-owned platforms. The total amount spent on these ads was at least twice as high as the amount spent during the January elections (some 30,000 USD in these elections, for some 2,600 ads, compared to around 16,000 USD in January elections, for some 1,740 ads).
Similar to previous monitoring, disinformation campaign played its negative role also during the local elections campaign. A need to introduce a workable online mechanism and to increase digital media literacy is even more urgent after this campaign.
#Monitoring results
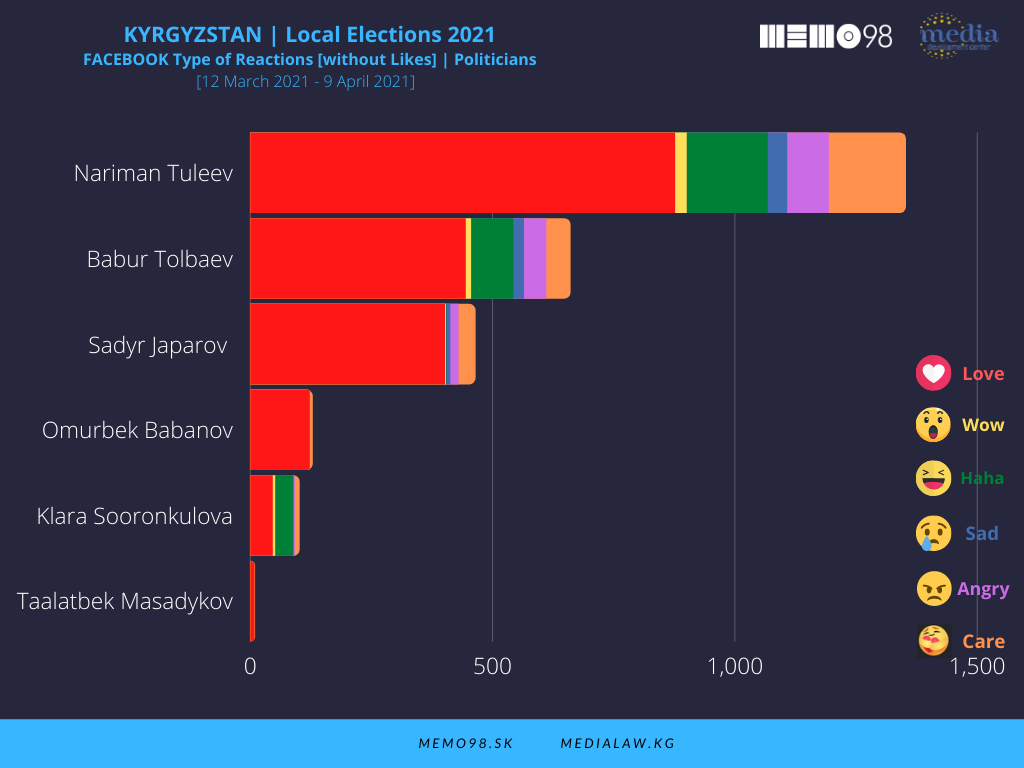
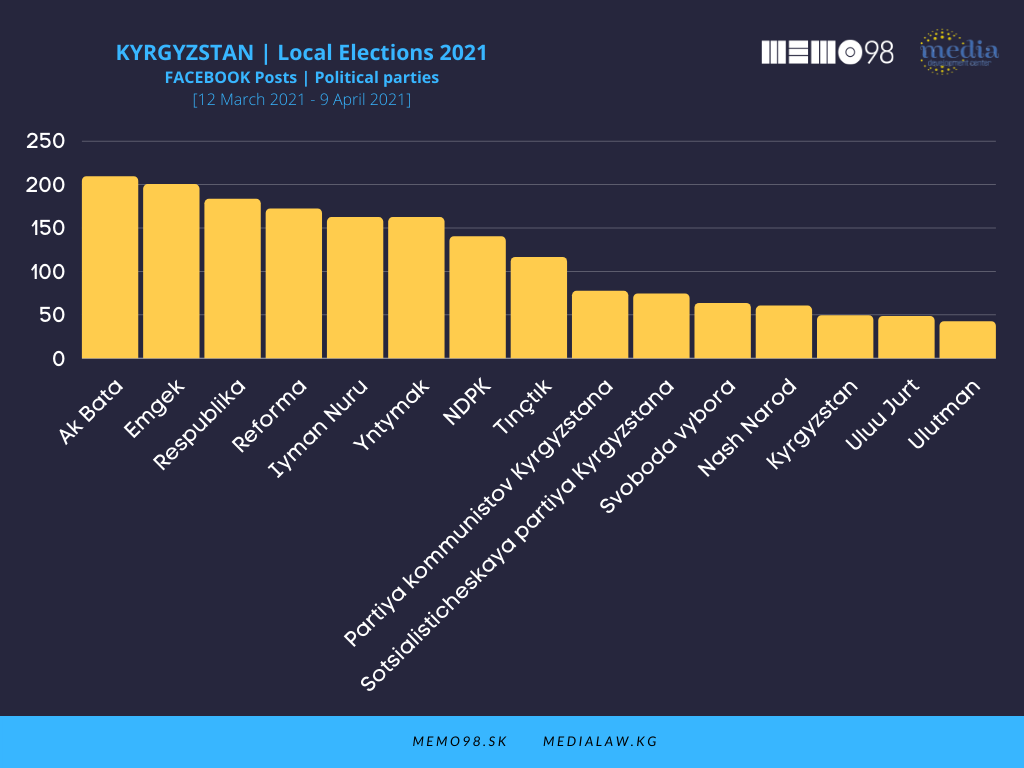
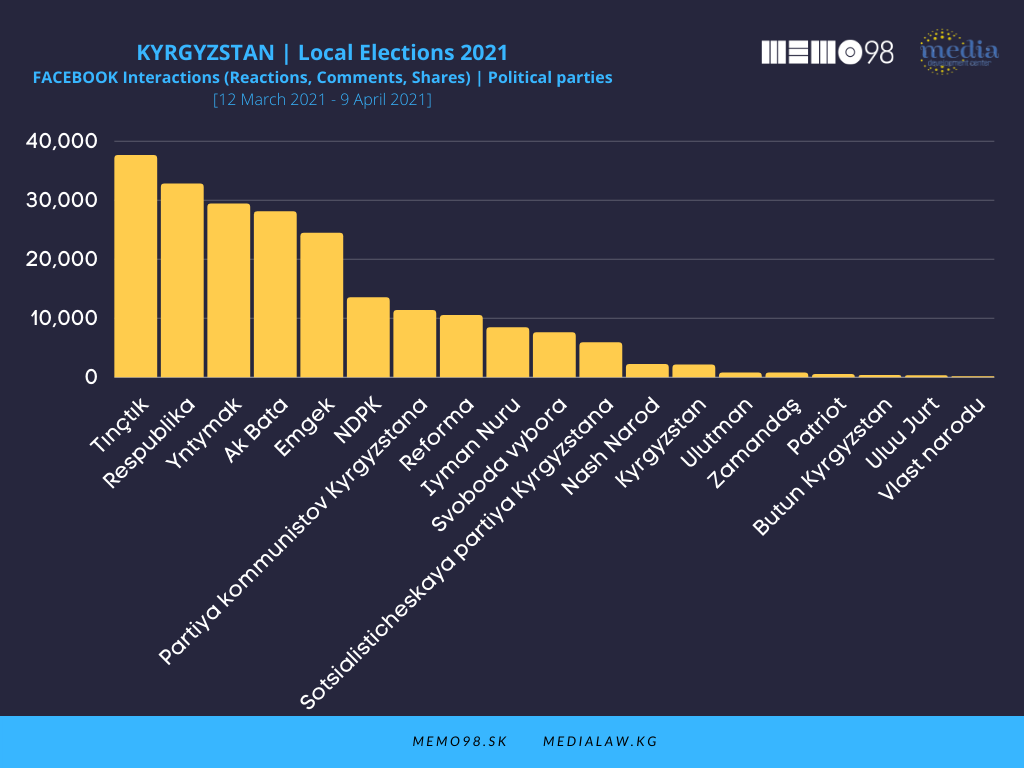
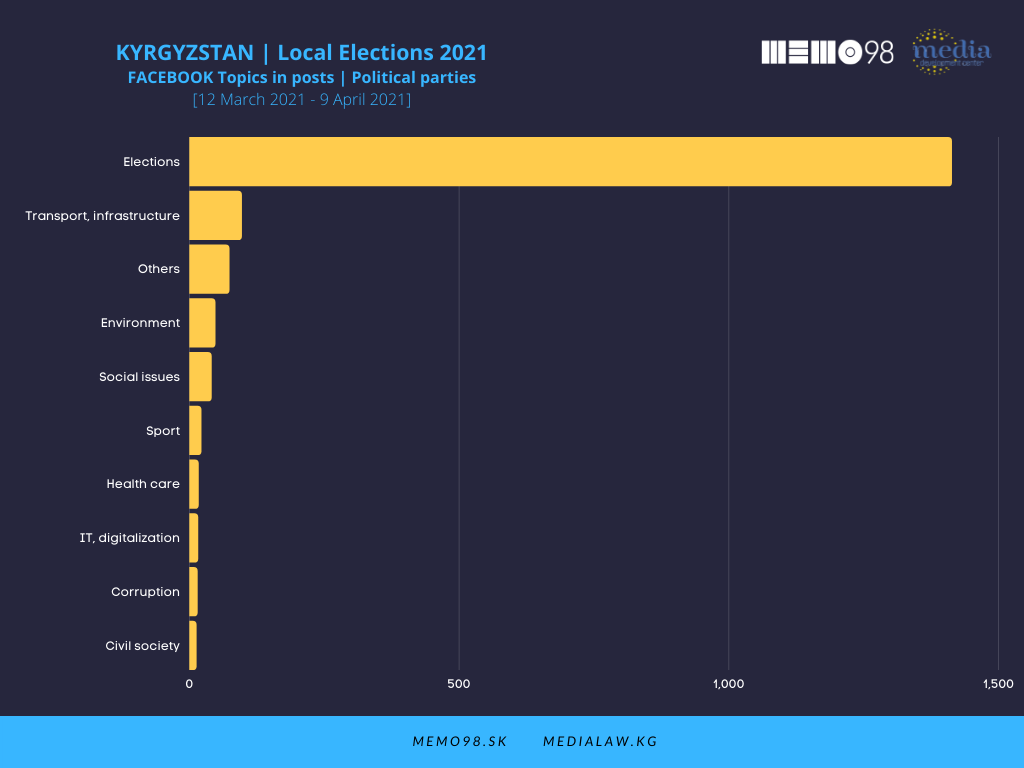

 \
\
The full report in English is available here and in Russian here.
The social media monitoring methodology was also developed thanks to the support from the Slovak Agency for International Development Cooperation. The Fund for Goods/ Services enabled by the Slovak Agency for International Development Cooperation.